|
BEWARE
They arrived together. The two women, in their 30s, working in a private institution came because they suspected they had contracted a sexually transmitted infection. Why did they have such suspicions, asked the doctor at the clinic run by the National STD/AIDS Control Programme. Yes, they were both married and they each had a child. But both of them were also having extra-marital relationships with two others. Don't you feel guilty? Yes, they do, they conceded, while one added: Den meka pattern eka, explaining this was the trend now. Tested for sexually transmitted infections (STIs), one turned out to be negative but the other positive. She had gonorrhoea. Pleas to get her husband to come to the clinic for treatment were futile, because she feared what the outcome would be even though the doctor assured her that he will not indicate what the problem was. "In such situations at least four people are involved," says Dr. Shantha Hettiarachchi of the National HIV/AIDS Prevention Project. The husband, the wife, the person one partner is involved with and that person's spouse are all vulnerable, some even without knowing that they are exposed to these diseases. Those days, extra-marital affairs were "unusual" and frowned upon by society, but these days they seem to be "usual" and sadly accepted by society, he laments. A sexually transmitted disease is usually contracted through sexual intercourse and not by touching, kissing, through insects or the use of common items such as plates and cups or even toilet seats, he says. "You cannot get them through swimming pools or by bathing in rivers." The main method of transmission is through unprotected sexual contact, MediScene learns, with other modes being mother to child and through infected blood transfusions. Common STIs in Sri Lanka are: =Genital herpes
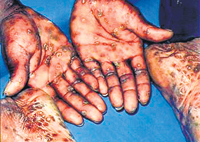
Ulcers in the genital region, a discharge from the genitals or lumps in the genital or anal region could be some of the signs that indicate a sexually transmitted infection, says Dr. Hettiarachchi. The STIs which cause ulcers: 1) Syphilis (primary) - Caused by a bacteria called Treponema Pallidum, an ulcer may develop within three months of exposure. Usually the person who has contracted the infection has a single deep, painless ulcer. There could also be painless, lymph node enlargement in the inguinal region. This is a curable disease. If the infection is not treated the ulcer may heal but the patient may develop secondary syphilis in a few months. Syphilis (secondary) - The symptoms are a skin rash, typically involving the palms and soles. Generalised, painless lymph nodes enlargement. Oral lesions and lumps in the genital region (condylomata lata).
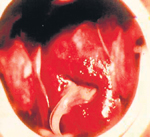
Late latent syphilis - No clinical features. Can be detected by blood tests (VDRL & TPHA). Most patients are detected in this stage of the disease, when taking blood tests for some other reason such as for foreign employment, antenatal investigations in pregnancy or voluntary testing. The infection can be cured if detected even at this stage. Syphilis (tertiary) - A few patients may develop cardiovascular syphilis (involving the heart and main blood vessels) or neurosyphilis (involving the central nervous system) after about 20 years of exposure, without treatment.Then it could be fatal. Syphilis can be transmitted from an infected mother to her newborn baby. 2) Genital herpes - Caused by the virus, Herpes Simplex, the clinical features may develop within a few days or a few weeks. There will be flu like symptoms before the development of ulcers. The vesicles appear first and develop into ulcers which are painful, superficial and multiple. There will also be painful enlargement of the lymph nodes in the inguinal region. There is treatment only to relieve the symptoms. Genital herpes may recur during the patient's whole life-time as it is a viral disease. When recurring, the patient will develop only a few ulcers. The factors which precipitate recurrences are fever, stress, anxiety, fatigue, menstruation, infections, pregnancy and some drugs. The infection of a newborn baby can be prevented if the obstetrician is aware of the mother's condition during her pregnancy. STIs which cause a genital discharge. 1) Gonorrhoea - Caused by the bacteria, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, the clinical manifestation in males is a continuous, yellowish urethral discharge in about two to seven days after exposure. There will also be a burning sensation while passing urine with frequent micturition (urination). Most females exposed to the infection will remain symptom-less. Such asymptomatic patients are diagnosed through a smear and culture test carried out on a specimen of the discharge. A few female patients will have a discoloured vaginal discharge, burning sensation while passing urine, frequent urination and vaginal bleeding in-between menstruation. Gonorrhoea is curable but if it is not treated, the infection can spread to neighbouring structures of the genitourinary tract. This may lead to infertility. This disease can be transmitted to a newborn baby, if the mother is infected. 2) Non gonococcal urethritis/cervicitis - Caused mainly by the bacteriae, Chlamydia trachomatis, the clinical manifestations are a urethral/vaginal discharge, burning sensation while passing urine, increased frequency of urination and lower abdominal/scrotal pain. The symptoms may develop within three weeks of exposure. This infection is treatable but if not neighbouring structures of the genitourinary tract can be infected and could lead to infertility. This too can be passed on from mother to baby. 3) Trichomoniasis - The parasite Trichomonas Vaginalis causes this infection, with symptoms appearing in females within 30 days of exposure. The clinical manifestations are a profuse, offensive and frothy vaginal discharge, itching and burning sensation while passing urine. This is a treatable disease. The STIs which cause lumps: Genital warts - Caused by the virus, Human Papilloma, lumps in various shapes and sizes will develop in the genital or anal region within six months of exposure. Genital warts can be removed with topical applications or surgery. The selection of the topical applications or type of treatment may differ according to the site and type of the warts and the condition of the patient. Genital warts may recur during the patient's life-time. Genital warts and cancer of the cervix in females are linked. Patients are likely to develop cytological changes in the cervix, therefore, early detection through a pap smear is essential to prevent cancer of the cervix. Complications of STIs - There could be systemic involvement if the infection is not treated properly at the right time. Recurrences of the disease, mainly in infections caused by viruses, could occur. There could also be mother-to-child transmission especially when the mother is not treated. STIs which can be transmitted from mother to child: 1) Congenital syphilis -The clinical manifestations in the baby would be a nasal discharge, nasal bleeding, skin rash and involvement of internal organs such as the heart, liver, spleen and bones. If the mother is diagnosed during pregnancy, the infection of the child can be prevented. The relevant blood tests are carried out at the antenatal clinics. 2) Gonorrhoea and Non gonococcal cervicitis (ophthalmia neonatarum) - The newborn child will be infected with these two conditions during delivery, if the mother is not treated. The clinical manifestations in the baby will be a purulent (yellowish) discharge and swelling and redness of the eye. If not treated in time, the baby could develop visual damage. Dealing with the gravity of STIs, Dr. Hettiarachchi urges that safe sex is of paramount importance. "Even in case someone is tempted to have a casual sexual encounter, then use a condom." However, his final advice on how to keep the danger of sexually transmitted disease at bay, is very simple -- Be faithful to one partner and have one faithful partner.
|
||||||
Copyright © 2006 Wijeya Newspapers
Ltd. All rights reserved. |